Current vision systems for robots and drones rely on 3D sensors that, although powerful, do not always keep up with the fast-paced, unpredictable movement of the real world. These systems often struggle to measure speed instantly or are too bulky and expensive for everyday use. Now, in a paper published in the journal Nature, scientists report how they have developed a 4D imaging sensor on a chip that creates 3D maps of an environment while simultaneously tracking the speed of moving objects.Current vision systems for robots and drones rely on 3D sensors that, although powerful, do not always keep up with the fast-paced, unpredictable movement of the real world. These systems often struggle to measure speed instantly or are too bulky and expensive for everyday use. Now, in a paper published in the journal Nature, scientists report how they have developed a 4D imaging sensor on a chip that creates 3D maps of an environment while simultaneously tracking the speed of moving objects.[#item_full_content]
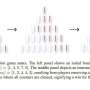
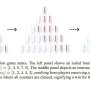
New research published in Machine Learning shows pattern learning is not enough to train AI to tackle games—and abstract representations or hybrid approaches may help. Many AI researchers describe game-playing as the “Formula 1” of AI: it’s a controlled test environment with clear rules and clear success criteria. This paper uses that idea as a diagnostic, by studying a very simple game Nim, a children’s matchstick game whose optimal strategy is known exactly.New research published in Machine Learning shows pattern learning is not enough to train AI to tackle games—and abstract representations or hybrid approaches may help. Many AI researchers describe game-playing as the “Formula 1” of AI: it’s a controlled test environment with clear rules and clear success criteria. This paper uses that idea as a diagnostic, by studying a very simple game Nim, a children’s matchstick game whose optimal strategy is known exactly.[#item_full_content]
New research published in Machine Learning shows pattern learning is not enough to train AI to tackle games—and abstract representations or hybrid approaches may help. Many AI researchers describe game-playing as the “Formula 1” of AI: it’s a controlled test environment with clear rules and clear success criteria. This paper uses that idea as a diagnostic, by studying a very simple game Nim, a children’s matchstick game whose optimal strategy is known exactly.New research published in Machine Learning shows pattern learning is not enough to train AI to tackle games—and abstract representations or hybrid approaches may help. Many AI researchers describe game-playing as the “Formula 1” of AI: it’s a controlled test environment with clear rules and clear success criteria. This paper uses that idea as a diagnostic, by studying a very simple game Nim, a children’s matchstick game whose optimal strategy is known exactly.Computer Sciences[#item_full_content]
Whether in the kitchen or on a workshop floor, robot assistants that can fetch items for people could be extremely useful. Now, a team of Brown University researchers has developed a way of making robots better at figuring out exactly which items a user might want them to retrieve.Whether in the kitchen or on a workshop floor, robot assistants that can fetch items for people could be extremely useful. Now, a team of Brown University researchers has developed a way of making robots better at figuring out exactly which items a user might want them to retrieve.[#item_full_content]
Chinese entrepreneur Frank Gao used to spend long hours running his social media accounts but now outsources the chore to AI agent tool OpenClaw, which is taking the country by storm despite official warnings over cybersecurity.Chinese entrepreneur Frank Gao used to spend long hours running his social media accounts but now outsources the chore to AI agent tool OpenClaw, which is taking the country by storm despite official warnings over cybersecurity.Machine learning & AI[#item_full_content]
AI-powered toys that “talk” with young children should be more tightly regulated and carry new safety kitemarks, according to a report that warns they are not always developed with children’s psychological safety in mind. The recommendation appears in the initial report from “AI in the Early Years”: a University of Cambridge project and the first systematic study of how Generative AI (GenAI) toys capable of human-like conversation may influence development in the critical years up to age five.AI-powered toys that “talk” with young children should be more tightly regulated and carry new safety kitemarks, according to a report that warns they are not always developed with children’s psychological safety in mind. The recommendation appears in the initial report from “AI in the Early Years”: a University of Cambridge project and the first systematic study of how Generative AI (GenAI) toys capable of human-like conversation may influence development in the critical years up to age five.Consumer & Gadgets[#item_full_content]
A robot that can locate lost items on command, the latest development at the Technical University of Munich (TUM), combines knowledge from the internet with a spatial map of its surroundings to efficiently find the objects being sought. The new robot from Prof. Angela Schoellig’s TUM Learning Systems and Robotics Lab looks like a broomstick on wheels with a camera mounted at the top. It is one of the first robots that not only integrates image understanding but also applies it to a clearly defined task.A robot that can locate lost items on command, the latest development at the Technical University of Munich (TUM), combines knowledge from the internet with a spatial map of its surroundings to efficiently find the objects being sought. The new robot from Prof. Angela Schoellig’s TUM Learning Systems and Robotics Lab looks like a broomstick on wheels with a camera mounted at the top. It is one of the first robots that not only integrates image understanding but also applies it to a clearly defined task.Robotics[#item_full_content]
A robot that can locate lost items on command, the latest development at the Technical University of Munich (TUM), combines knowledge from the internet with a spatial map of its surroundings to efficiently find the objects being sought. The new robot from Prof. Angela Schoellig’s TUM Learning Systems and Robotics Lab looks like a broomstick on wheels with a camera mounted at the top. It is one of the first robots that not only integrates image understanding but also applies it to a clearly defined task.A robot that can locate lost items on command, the latest development at the Technical University of Munich (TUM), combines knowledge from the internet with a spatial map of its surroundings to efficiently find the objects being sought. The new robot from Prof. Angela Schoellig’s TUM Learning Systems and Robotics Lab looks like a broomstick on wheels with a camera mounted at the top. It is one of the first robots that not only integrates image understanding but also applies it to a clearly defined task.[#item_full_content]
Most of you have used a navigation app like Google Maps for your travels at some point. These apps rely on algorithms that compute shortest paths through vast networks. Now imagine scaling that task to calculate distances between every pair of points in a massive system, for example, a transportation grid, a communication backbone, or even a biological network such as protein or neural interaction networks.Most of you have used a navigation app like Google Maps for your travels at some point. These apps rely on algorithms that compute shortest paths through vast networks. Now imagine scaling that task to calculate distances between every pair of points in a massive system, for example, a transportation grid, a communication backbone, or even a biological network such as protein or neural interaction networks.[#item_full_content]
Imagine it is two weeks before a major election in a closely contested state. A controversial ballot measure is on the line. Suddenly, a wave of posts floods X, Reddit, and Facebook, all pushing the same narrative, all amplifying each other, all generating the appearance of a massive grassroots movement. Except none of it is real.Imagine it is two weeks before a major election in a closely contested state. A controversial ballot measure is on the line. Suddenly, a wave of posts floods X, Reddit, and Facebook, all pushing the same narrative, all amplifying each other, all generating the appearance of a massive grassroots movement. Except none of it is real.Security[#item_full_content]