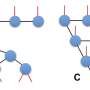
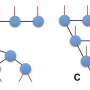
Deep machine learning has achieved remarkable success in various fields of artificial intelligence, but achieving both high interpretability and high efficiency simultaneously remains a critical challenge. Shi-Ju Ran of Capital Normal University and Gang Su of the University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have reviewed an innovative approach based on tensor networks, drawing inspiration from quantum mechanics. This approach offers a promising solution to the long-standing challenge of reconciling interpretability and efficiency in deep machine learning.Deep machine learning has achieved remarkable success in various fields of artificial intelligence, but achieving both high interpretability and high efficiency simultaneously remains a critical challenge. Shi-Ju Ran of Capital Normal University and Gang Su of the University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have reviewed an innovative approach based on tensor networks, drawing inspiration from quantum mechanics. This approach offers a promising solution to the long-standing challenge of reconciling interpretability and efficiency in deep machine learning.[#item_full_content]
Deep machine learning has achieved remarkable success in various fields of artificial intelligence, but achieving both high interpretability and high efficiency simultaneously remains a critical challenge. Shi-Ju Ran of Capital Normal University and Gang Su of the University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have reviewed an innovative approach based on tensor networks, drawing inspiration from quantum mechanics. This approach offers a promising solution to the long-standing challenge of reconciling interpretability and efficiency in deep machine learning.Deep machine learning has achieved remarkable success in various fields of artificial intelligence, but achieving both high interpretability and high efficiency simultaneously remains a critical challenge. Shi-Ju Ran of Capital Normal University and Gang Su of the University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have reviewed an innovative approach based on tensor networks, drawing inspiration from quantum mechanics. This approach offers a promising solution to the long-standing challenge of reconciling interpretability and efficiency in deep machine learning.Computer Sciences[#item_full_content]
As the high-speed railway network in China extends beyond 40,000 kilometers, maintaining seamless internet connectivity for passengers is becoming increasingly challenging. The demand for consistent and reliable online access is particularly crucial for travelers who spend extended hours on trains, relying on the expectation of undisturbed work, study, or entertainment. Addressing this need, a team of researchers from the School of Computer Science at Peking University has developed “HiMoDiag”—an innovative tool designed to enhance the understanding and management of network performance in extremely high-mobility scenarios.As the high-speed railway network in China extends beyond 40,000 kilometers, maintaining seamless internet connectivity for passengers is becoming increasingly challenging. The demand for consistent and reliable online access is particularly crucial for travelers who spend extended hours on trains, relying on the expectation of undisturbed work, study, or entertainment. Addressing this need, a team of researchers from the School of Computer Science at Peking University has developed “HiMoDiag”—an innovative tool designed to enhance the understanding and management of network performance in extremely high-mobility scenarios.[#item_full_content]
Image recognition technology has come a long way since 2012 when a group of computer scientists at the University of Toronto created a convolutional neural network (CNN)—dubbed “AlexNet” after its creator Alex Krizhevsky—that correctly identified images much better than others. Its findings have propelled successful use of CNNs in related fields such as video analysis and pattern recognition, and now researchers are now focusing on 3D deep learning networks.Image recognition technology has come a long way since 2012 when a group of computer scientists at the University of Toronto created a convolutional neural network (CNN)—dubbed “AlexNet” after its creator Alex Krizhevsky—that correctly identified images much better than others. Its findings have propelled successful use of CNNs in related fields such as video analysis and pattern recognition, and now researchers are now focusing on 3D deep learning networks.[#item_full_content]
Image recognition technology has come a long way since 2012 when a group of computer scientists at the University of Toronto created a convolutional neural network (CNN)—dubbed “AlexNet” after its creator Alex Krizhevsky—that correctly identified images much better than others. Its findings have propelled successful use of CNNs in related fields such as video analysis and pattern recognition, and now researchers are now focusing on 3D deep learning networks.Image recognition technology has come a long way since 2012 when a group of computer scientists at the University of Toronto created a convolutional neural network (CNN)—dubbed “AlexNet” after its creator Alex Krizhevsky—that correctly identified images much better than others. Its findings have propelled successful use of CNNs in related fields such as video analysis and pattern recognition, and now researchers are now focusing on 3D deep learning networks.Computer Sciences[#item_full_content]
Recent advances in generative artificial intelligence have spurred developments in realistic speech synthesis. While this technology has the potential to improve lives through personalized voice assistants and accessibility-enhancing communication tools, it also has led to the emergence of deepfakes, in which synthesized speech can be misused to deceive humans and machines for nefarious purposes.Recent advances in generative artificial intelligence have spurred developments in realistic speech synthesis. While this technology has the potential to improve lives through personalized voice assistants and accessibility-enhancing communication tools, it also has led to the emergence of deepfakes, in which synthesized speech can be misused to deceive humans and machines for nefarious purposes.Security[#item_full_content]
Influencing the U.S. election or the U.K.’s political future by using a combination of the personal information posted on Facebook by millions of people and powerful data analysis technology—it wasn’t that long ago that this would have seemed like something out of a sci-fi novel, but the 2018 Cambridge Analytica scandal proved that it can happen and that, as a result of advancing technology and machine intelligence, we are now facing fundamental dilemmas that we never had to think about before.Influencing the U.S. election or the U.K.’s political future by using a combination of the personal information posted on Facebook by millions of people and powerful data analysis technology—it wasn’t that long ago that this would have seemed like something out of a sci-fi novel, but the 2018 Cambridge Analytica scandal proved that it can happen and that, as a result of advancing technology and machine intelligence, we are now facing fundamental dilemmas that we never had to think about before.Security[#item_full_content]
Researchers have developed a self-healing robotic gripper for use in soft robotics that is adaptable, recyclable and resilient to damage, thanks to heat-assisted autonomous healing.Researchers have developed a self-healing robotic gripper for use in soft robotics that is adaptable, recyclable and resilient to damage, thanks to heat-assisted autonomous healing.[#item_full_content]
In the real world/digital world cross-over of mixed reality, a user’s immersive engagement with the program is called presence. Now, UMass Amherst researchers are the first to identify reaction time as a potential presence measurement tool. Their findings, published in IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, have implications for calibrating mixed reality to the user in real time.In the real world/digital world cross-over of mixed reality, a user’s immersive engagement with the program is called presence. Now, UMass Amherst researchers are the first to identify reaction time as a potential presence measurement tool. Their findings, published in IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, have implications for calibrating mixed reality to the user in real time.[#item_full_content]
In a study published in Scientific Reports, a research team from the University of Passau compared the quality of machine-generated content with essays written by secondary school students. The upshot: The AI-based chatbot performed better across all criteria, especially when it came to language mastery.In a study published in Scientific Reports, a research team from the University of Passau compared the quality of machine-generated content with essays written by secondary school students. The upshot: The AI-based chatbot performed better across all criteria, especially when it came to language mastery.[#item_full_content]