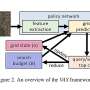
When combating complex problems like illegal poaching and human trafficking, efficient yet broad geospatial search tools can provide critical assistance in finding and stopping the activity. A visual active search (VAS) framework for geospatial exploration developed by researchers in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis uses a novel visual reasoning model and aerial imagery to learn how to search for objects more effectively.When combating complex problems like illegal poaching and human trafficking, efficient yet broad geospatial search tools can provide critical assistance in finding and stopping the activity. A visual active search (VAS) framework for geospatial exploration developed by researchers in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis uses a novel visual reasoning model and aerial imagery to learn how to search for objects more effectively.[#item_full_content]
When combating complex problems like illegal poaching and human trafficking, efficient yet broad geospatial search tools can provide critical assistance in finding and stopping the activity. A visual active search (VAS) framework for geospatial exploration developed by researchers in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis uses a novel visual reasoning model and aerial imagery to learn how to search for objects more effectively.When combating complex problems like illegal poaching and human trafficking, efficient yet broad geospatial search tools can provide critical assistance in finding and stopping the activity. A visual active search (VAS) framework for geospatial exploration developed by researchers in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis uses a novel visual reasoning model and aerial imagery to learn how to search for objects more effectively.Computer Sciences[#item_full_content]
A team of AI researchers at Microsoft working with colleagues from Pacific Northwest National Laboratory has used AI to develop a battery that uses less lithium. Together, they have published a paper describing their work on the arXiv preprint server.A team of AI researchers at Microsoft working with colleagues from Pacific Northwest National Laboratory has used AI to develop a battery that uses less lithium. Together, they have published a paper describing their work on the arXiv preprint server.Energy & Green Tech[#item_full_content]
Recent numerical studies investigating neural networks have found that solutions typically found by modern machine learning algorithms lie in complex extended regions of the loss landscape. In these regions, zero-energy paths between pairs of distant solutions can be established.Recent numerical studies investigating neural networks have found that solutions typically found by modern machine learning algorithms lie in complex extended regions of the loss landscape. In these regions, zero-energy paths between pairs of distant solutions can be established.[#item_full_content]
Recent numerical studies investigating neural networks have found that solutions typically found by modern machine learning algorithms lie in complex extended regions of the loss landscape. In these regions, zero-energy paths between pairs of distant solutions can be established.Recent numerical studies investigating neural networks have found that solutions typically found by modern machine learning algorithms lie in complex extended regions of the loss landscape. In these regions, zero-energy paths between pairs of distant solutions can be established.Computer Sciences[#item_full_content]
An AI (artificial intelligence) technology for robot work, which allows robots to be easily applied to manufacturing processes, has been developed for the first time in the world. The newly developed technology can be used in a variety of processes, such as the manufacturing of automobiles and machine parts, as well as assembly and production, and is expected to contribute to the improvement of the working environment at manufacturing sites in the future.An AI (artificial intelligence) technology for robot work, which allows robots to be easily applied to manufacturing processes, has been developed for the first time in the world. The newly developed technology can be used in a variety of processes, such as the manufacturing of automobiles and machine parts, as well as assembly and production, and is expected to contribute to the improvement of the working environment at manufacturing sites in the future.Robotics[#item_full_content]
Uncertainty estimation is critical to improving the reliability of deep neural networks. A research team led by Aydogan Ozcan at the University of California, Los Angeles, has introduced an uncertainty quantification method that uses cycle consistency to enhance the reliability of deep neural networks in solving inverse imaging problems.Uncertainty estimation is critical to improving the reliability of deep neural networks. A research team led by Aydogan Ozcan at the University of California, Los Angeles, has introduced an uncertainty quantification method that uses cycle consistency to enhance the reliability of deep neural networks in solving inverse imaging problems.Machine learning & AI[#item_full_content]
University of Copenhagen researchers have developed software able to disguise sensitive data such as those used for machine learning in health care applications. The method protects privacy while making datasets available for the development of better treatments.University of Copenhagen researchers have developed software able to disguise sensitive data such as those used for machine learning in health care applications. The method protects privacy while making datasets available for the development of better treatments.Software[#item_full_content]
The image spoke for itself. University at Buffalo computer scientist and deepfake expert Siwei Lyu created a photo collage out of the hundreds of faces that his detection algorithms had incorrectly classified as fake—and the new composition clearly had a predominantly darker skin tone.The image spoke for itself. University at Buffalo computer scientist and deepfake expert Siwei Lyu created a photo collage out of the hundreds of faces that his detection algorithms had incorrectly classified as fake—and the new composition clearly had a predominantly darker skin tone.[#item_full_content]
The image spoke for itself. University at Buffalo computer scientist and deepfake expert Siwei Lyu created a photo collage out of the hundreds of faces that his detection algorithms had incorrectly classified as fake—and the new composition clearly had a predominantly darker skin tone.The image spoke for itself. University at Buffalo computer scientist and deepfake expert Siwei Lyu created a photo collage out of the hundreds of faces that his detection algorithms had incorrectly classified as fake—and the new composition clearly had a predominantly darker skin tone.Computer Sciences[#item_full_content]