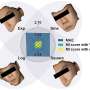
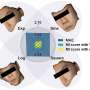
In a recent publication in Science China Life Sciences, a research team led by Professor Jing-Dong Jackie Han and Ph.D. student Xinyu Yang from Peking University established a deep learning model for age estimation using non-registered 3D face point clouds. They also proposed the coordinate-wise monotonic transformation algorithm to isolate age-related facial features from identifiable human faces.In a recent publication in Science China Life Sciences, a research team led by Professor Jing-Dong Jackie Han and Ph.D. student Xinyu Yang from Peking University established a deep learning model for age estimation using non-registered 3D face point clouds. They also proposed the coordinate-wise monotonic transformation algorithm to isolate age-related facial features from identifiable human faces.[#item_full_content]
In a recent publication in Science China Life Sciences, a research team led by Professor Jing-Dong Jackie Han and Ph.D. student Xinyu Yang from Peking University established a deep learning model for age estimation using non-registered 3D face point clouds. They also proposed the coordinate-wise monotonic transformation algorithm to isolate age-related facial features from identifiable human faces.In a recent publication in Science China Life Sciences, a research team led by Professor Jing-Dong Jackie Han and Ph.D. student Xinyu Yang from Peking University established a deep learning model for age estimation using non-registered 3D face point clouds. They also proposed the coordinate-wise monotonic transformation algorithm to isolate age-related facial features from identifiable human faces.Computer Sciences[#item_full_content]
We use computers to help us make (hopefully) unbiased decisions. The problem is that machine-learning algorithms do not always make fair classifications if human bias is embedded in the data used to train them—which is often the case in practice.We use computers to help us make (hopefully) unbiased decisions. The problem is that machine-learning algorithms do not always make fair classifications if human bias is embedded in the data used to train them—which is often the case in practice.[#item_full_content]
We use computers to help us make (hopefully) unbiased decisions. The problem is that machine-learning algorithms do not always make fair classifications if human bias is embedded in the data used to train them—which is often the case in practice.We use computers to help us make (hopefully) unbiased decisions. The problem is that machine-learning algorithms do not always make fair classifications if human bias is embedded in the data used to train them—which is often the case in practice.Computer Sciences[#item_full_content]
While the class imbalance issue has been extensively investigated within the multi-class paradigm, its study in the multi-dimensional classification (MDC) context has been limited due to the imbalance shift phenomenon. A sample’s classification as a minor or major class instance becomes ambiguous when it belongs to a minor class in one labeling dimension (LD) and a major class in another.While the class imbalance issue has been extensively investigated within the multi-class paradigm, its study in the multi-dimensional classification (MDC) context has been limited due to the imbalance shift phenomenon. A sample’s classification as a minor or major class instance becomes ambiguous when it belongs to a minor class in one labeling dimension (LD) and a major class in another.[#item_full_content]
The rise of commercially viable generative artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to transform a vast range of sectors. This transformation will be particularly profound in contemporary military education.The rise of commercially viable generative artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to transform a vast range of sectors. This transformation will be particularly profound in contemporary military education.Machine learning & AI[#item_full_content]
A new paper from researchers at Oxford Internet Institute, University of Oxford, highlights the benefits and risks of personalizing Large Language Models (LLMS) to their users.A new paper from researchers at Oxford Internet Institute, University of Oxford, highlights the benefits and risks of personalizing Large Language Models (LLMS) to their users.Machine learning & AI[#item_full_content]
Setting the stage for a new era of immersive displays, researchers are one step closer to mixing the real and virtual worlds in an ordinary pair of eyeglasses using high-definition 3D holographic images, according to a study led by Princeton University researchers.Setting the stage for a new era of immersive displays, researchers are one step closer to mixing the real and virtual worlds in an ordinary pair of eyeglasses using high-definition 3D holographic images, according to a study led by Princeton University researchers.[#item_full_content]
Machine learning-based models that can autonomously generate various types of content have become increasingly advanced over the past few years. These frameworks have opened new possibilities for filmmaking and for compiling datasets to train robotics algorithms.Machine learning-based models that can autonomously generate various types of content have become increasingly advanced over the past few years. These frameworks have opened new possibilities for filmmaking and for compiling datasets to train robotics algorithms.Machine learning & AI[#item_full_content]
Alex Popken was a longtime trust and safety executive at Twitter focusing on content moderation before leaving in 2023. She was the first employee there dedicated to moderating Twitter’s advertising business when she started in 2013.Alex Popken was a longtime trust and safety executive at Twitter focusing on content moderation before leaving in 2023. She was the first employee there dedicated to moderating Twitter’s advertising business when she started in 2013.Business[#item_full_content]