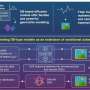
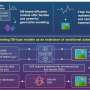
A new framework for generative diffusion models was developed by researchers at Science Tokyo, significantly improving generative AI models. The method reinterpreted Schrödinger bridge models as variational autoencoders with infinitely many latent variables, reducing computational costs and preventing overfitting. By appropriately interrupting the training of the encoder, this approach enabled development of more efficient generative AI, with broad applicability beyond standard diffusion models.A new framework for generative diffusion models was developed by researchers at Science Tokyo, significantly improving generative AI models. The method reinterpreted Schrödinger bridge models as variational autoencoders with infinitely many latent variables, reducing computational costs and preventing overfitting. By appropriately interrupting the training of the encoder, this approach enabled development of more efficient generative AI, with broad applicability beyond standard diffusion models.[#item_full_content]
A new framework for generative diffusion models was developed by researchers at Science Tokyo, significantly improving generative AI models. The method reinterpreted Schrödinger bridge models as variational autoencoders with infinitely many latent variables, reducing computational costs and preventing overfitting. By appropriately interrupting the training of the encoder, this approach enabled development of more efficient generative AI, with broad applicability beyond standard diffusion models.A new framework for generative diffusion models was developed by researchers at Science Tokyo, significantly improving generative AI models. The method reinterpreted Schrödinger bridge models as variational autoencoders with infinitely many latent variables, reducing computational costs and preventing overfitting. By appropriately interrupting the training of the encoder, this approach enabled development of more efficient generative AI, with broad applicability beyond standard diffusion models.Computer Sciences[#item_full_content]
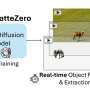
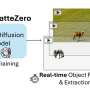
Bar-Ilan University announced today that a team from its Department of Computer Science has developed a breakthrough in video processing that significantly simplifies the separation of foreground objects from their backgrounds, without the need for extensive training or optimization. The new method, called OmnimatteZero, was developed by Dr. Dvir Samuel and Prof. Gal Chechik, who also serves as a senior director of AI research at NVIDIA. The paper is published on the arXiv preprint server.Bar-Ilan University announced today that a team from its Department of Computer Science has developed a breakthrough in video processing that significantly simplifies the separation of foreground objects from their backgrounds, without the need for extensive training or optimization. The new method, called OmnimatteZero, was developed by Dr. Dvir Samuel and Prof. Gal Chechik, who also serves as a senior director of AI research at NVIDIA. The paper is published on the arXiv preprint server.[#item_full_content]
Bar-Ilan University announced today that a team from its Department of Computer Science has developed a breakthrough in video processing that significantly simplifies the separation of foreground objects from their backgrounds, without the need for extensive training or optimization. The new method, called OmnimatteZero, was developed by Dr. Dvir Samuel and Prof. Gal Chechik, who also serves as a senior director of AI research at NVIDIA. The paper is published on the arXiv preprint server.Bar-Ilan University announced today that a team from its Department of Computer Science has developed a breakthrough in video processing that significantly simplifies the separation of foreground objects from their backgrounds, without the need for extensive training or optimization. The new method, called OmnimatteZero, was developed by Dr. Dvir Samuel and Prof. Gal Chechik, who also serves as a senior director of AI research at NVIDIA. The paper is published on the arXiv preprint server.Computer Sciences[#item_full_content]
Lithium-ion batteries power most electronics, but they have limited energy density—they can store only a certain amount of energy per mass or volume of the battery.Lithium-ion batteries power most electronics, but they have limited energy density—they can store only a certain amount of energy per mass or volume of the battery.Energy & Green Tech[#item_full_content]
A German music rights body is suing OpenAI for copyright infringement, claiming the US tech giant’s AI systems reproduced several artists’ lyrics without permission, a court heard Monday.A German music rights body is suing OpenAI for copyright infringement, claiming the US tech giant’s AI systems reproduced several artists’ lyrics without permission, a court heard Monday.Business[#item_full_content]
When you don’t have the money for a lawyer to represent you in a court case, even judges can understand the temptation to get free help from anywhere—including tapping into generative artificial intelligence (AI).When you don’t have the money for a lawyer to represent you in a court case, even judges can understand the temptation to get free help from anywhere—including tapping into generative artificial intelligence (AI).Consumer & Gadgets[#item_full_content]
Vibe coding Anything nabs a $100M valuation, after hitting $2M ARR in its first two weeks
Anything raised an $11 million funding round at a $100 million valuation.Anything raised an $11 million funding round at a $100 million valuation.[#item_full_content]
In the rush to cash in on the generative artificial intelligence gold rush, one possible outcome of AI’s future rarely gets discussed: what if the technology never works well enough to replace your co-workers, companies fail to use AI well or most AI startups simply fail?In the rush to cash in on the generative artificial intelligence gold rush, one possible outcome of AI’s future rarely gets discussed: what if the technology never works well enough to replace your co-workers, companies fail to use AI well or most AI startups simply fail?Business[#item_full_content]
Insurance is based on a principle of solidarity, but that is now being undermined by the algorithms used to build our profiles.Insurance is based on a principle of solidarity, but that is now being undermined by the algorithms used to build our profiles.Business[#item_full_content]