Most of you have used a navigation app like Google Maps for your travels at some point. These apps rely on algorithms that compute shortest paths through vast networks. Now imagine scaling that task to calculate distances between every pair of points in a massive system, for example, a transportation grid, a communication backbone, or even a biological network such as protein or neural interaction networks.Most of you have used a navigation app like Google Maps for your travels at some point. These apps rely on algorithms that compute shortest paths through vast networks. Now imagine scaling that task to calculate distances between every pair of points in a massive system, for example, a transportation grid, a communication backbone, or even a biological network such as protein or neural interaction networks.[#item_full_content]
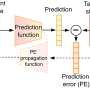
Over the past decades, computer scientists have developed numerous artificial intelligence (AI) systems that can process human speech in different languages. The extent to which these models replicate the brain processes via which humans understand spoken language, however, has not yet been clearly determined.Over the past decades, computer scientists have developed numerous artificial intelligence (AI) systems that can process human speech in different languages. The extent to which these models replicate the brain processes via which humans understand spoken language, however, has not yet been clearly determined.[#item_full_content]
AI chatbots are standardizing how people speak, write, and think. If this homogenization continues unchecked, it risks reducing humanity’s collective wisdom and ability to adapt, computer scientists and psychologists argue in an opinion paper published in Trends in Cognitive Sciences.AI chatbots are standardizing how people speak, write, and think. If this homogenization continues unchecked, it risks reducing humanity’s collective wisdom and ability to adapt, computer scientists and psychologists argue in an opinion paper published in Trends in Cognitive Sciences.[#item_full_content]
To stay up to date and work forward in their fields, scientists must have at their fingertips and in their minds thousands of published studies. Large language models (LLMs) show promise as a tool for exploring the vast scientific literature, but are they trustworthy when it comes to providing full and scientifically accurate answers to complex questions in specialized fields?To stay up to date and work forward in their fields, scientists must have at their fingertips and in their minds thousands of published studies. Large language models (LLMs) show promise as a tool for exploring the vast scientific literature, but are they trustworthy when it comes to providing full and scientifically accurate answers to complex questions in specialized fields?[#item_full_content]
For years, the guiding assumption of artificial intelligence has been simple: an AI is only as good as the data it has seen. Feed it more, train it longer, and it performs better. Feed it less, and it stumbles. A new study from the USC Viterbi School of Engineering was accepted at the IEEE SoutheastCon 2026, taking place March 12–15. It suggests something far more surprising: with the right method in place, an AI model can dramatically improve its performance in territory it was barely trained on, pushing well past what its training data alone would ever allow.For years, the guiding assumption of artificial intelligence has been simple: an AI is only as good as the data it has seen. Feed it more, train it longer, and it performs better. Feed it less, and it stumbles. A new study from the USC Viterbi School of Engineering was accepted at the IEEE SoutheastCon 2026, taking place March 12–15. It suggests something far more surprising: with the right method in place, an AI model can dramatically improve its performance in territory it was barely trained on, pushing well past what its training data alone would ever allow.[#item_full_content]
Researchers at the University at Albany and Rutgers University have developed an early-warning framework that can predict harmful social media interactions before they erupt, paving the way for interventions that can minimize harm and make platforms safer for users. Using publicly available datasets from Reddit and Instagram, two social media platforms with distinct conversation dynamics, researchers trained models to predict from just the first 10 comments whether a thread would escalate into “concentrated waves of toxic interactions”—or what they have dubbed a “negative storm” or “neg storm.”Researchers at the University at Albany and Rutgers University have developed an early-warning framework that can predict harmful social media interactions before they erupt, paving the way for interventions that can minimize harm and make platforms safer for users. Using publicly available datasets from Reddit and Instagram, two social media platforms with distinct conversation dynamics, researchers trained models to predict from just the first 10 comments whether a thread would escalate into “concentrated waves of toxic interactions”—or what they have dubbed a “negative storm” or “neg storm.”[#item_full_content]
Artificial intelligence now plays Go, paints pictures, and even converses like a human. However, there remains a decisive difference: AI requires far more electricity than the human brain to operate. Scientists have long asked the question, “How can the brain learn so intelligently using so little energy?” KAIST researchers have moved one step closer to the answer.Artificial intelligence now plays Go, paints pictures, and even converses like a human. However, there remains a decisive difference: AI requires far more electricity than the human brain to operate. Scientists have long asked the question, “How can the brain learn so intelligently using so little energy?” KAIST researchers have moved one step closer to the answer.[#item_full_content]
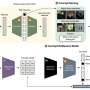
In high-stakes settings like medical diagnostics, users often want to know what led a computer vision model to make a certain prediction, so they can determine whether to trust its output. Concept bottleneck modeling is one method that enables artificial intelligence systems to explain their decision-making process. These methods force a deep-learning model to use a set of concepts, which can be understood by humans, to make a prediction. In new research, MIT computer scientists developed a method that coaxes the model to achieve better accuracy and clearer, more concise explanations.In high-stakes settings like medical diagnostics, users often want to know what led a computer vision model to make a certain prediction, so they can determine whether to trust its output. Concept bottleneck modeling is one method that enables artificial intelligence systems to explain their decision-making process. These methods force a deep-learning model to use a set of concepts, which can be understood by humans, to make a prediction. In new research, MIT computer scientists developed a method that coaxes the model to achieve better accuracy and clearer, more concise explanations.[#item_full_content]
At least 57 nations have live antipersonnel land mines in their territories. In 2024 alone, 1,945 people were killed by mines and 4,325 were injured, 90% of whom were civilians. Nearly half of those were children. Demining operations removed 105,640 mines in the same year.At least 57 nations have live antipersonnel land mines in their territories. In 2024 alone, 1,945 people were killed by mines and 4,325 were injured, 90% of whom were civilians. Nearly half of those were children. Demining operations removed 105,640 mines in the same year.[#item_full_content]
When artificial intelligence systems began acing long-standing academic assessments, researchers realized they had a problem: the tests were too easy. Popular evaluations, such as the Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU) exam, once considered formidable, are no longer challenging enough to meaningfully test advanced AI systems.When artificial intelligence systems began acing long-standing academic assessments, researchers realized they had a problem: the tests were too easy. Popular evaluations, such as the Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU) exam, once considered formidable, are no longer challenging enough to meaningfully test advanced AI systems.[#item_full_content]