When writing program code, software developers often work in pairs—a practice that reduces errors and encourages knowledge sharing. Increasingly, AI assistants are now being used for this role.When writing program code, software developers often work in pairs—a practice that reduces errors and encourages knowledge sharing. Increasingly, AI assistants are now being used for this role.[#item_full_content]
New research from Carnegie Mellon University’s School of Computer Science shows that the smarter the artificial intelligence system, the more selfish it will act.New research from Carnegie Mellon University’s School of Computer Science shows that the smarter the artificial intelligence system, the more selfish it will act.[#item_full_content]
Analog computers are systems that perform computations by manipulating physical quantities such as electrical current, that map math variables, instead of representing information using abstraction with discrete binary values (i.e., 0 or 1), like digital computers.Analog computers are systems that perform computations by manipulating physical quantities such as electrical current, that map math variables, instead of representing information using abstraction with discrete binary values (i.e., 0 or 1), like digital computers.[#item_full_content]
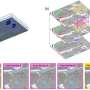
The Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS) has developed an artificial intelligence (AI)-based image segmentation algorithm that can rapidly reconstruct three-dimensional (3D) structures from two-dimensional (2D) cross-sectional images of biological samples captured using a scanning electron microscope (SEM).The Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS) has developed an artificial intelligence (AI)-based image segmentation algorithm that can rapidly reconstruct three-dimensional (3D) structures from two-dimensional (2D) cross-sectional images of biological samples captured using a scanning electron microscope (SEM).[#item_full_content]
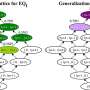
After the advent of ChatGPT, the use of large language models (LLMs) has become increasingly widespread worldwide. LLMs are artificial intelligence (AI) systems trained on large sets of written texts, which can rapidly process queries in various languages and generate responses that sometimes appear to be written by humans.After the advent of ChatGPT, the use of large language models (LLMs) has become increasingly widespread worldwide. LLMs are artificial intelligence (AI) systems trained on large sets of written texts, which can rapidly process queries in various languages and generate responses that sometimes appear to be written by humans.[#item_full_content]
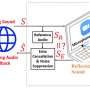
Since the COVID-19 pandemic, video conferencing platforms like Zoom and Microsoft Teams have become essential for work, education, and social connections. While these platforms offer controls such as disabling cameras and muting microphones to safeguard user privacy, a new study suggests that video conferencing may not be as secure as many assume.Since the COVID-19 pandemic, video conferencing platforms like Zoom and Microsoft Teams have become essential for work, education, and social connections. While these platforms offer controls such as disabling cameras and muting microphones to safeguard user privacy, a new study suggests that video conferencing may not be as secure as many assume.[#item_full_content]
Hand gesture controls being developed for the next generation of virtual and augmented reality systems risk excluding millions of people, including those with common conditions such as arthritis and carpal tunnel syndrome, as well as individuals with disabilities resulting from stroke, new research finds.Hand gesture controls being developed for the next generation of virtual and augmented reality systems risk excluding millions of people, including those with common conditions such as arthritis and carpal tunnel syndrome, as well as individuals with disabilities resulting from stroke, new research finds.[#item_full_content]
Computer programming powers modern society and enabled the AI revolution, but little is known about how our brains learn this essential skill. To help answer that question, Johns Hopkins University researchers studied the brain activity of university students before and after they learned how to code.Computer programming powers modern society and enabled the AI revolution, but little is known about how our brains learn this essential skill. To help answer that question, Johns Hopkins University researchers studied the brain activity of university students before and after they learned how to code.[#item_full_content]
Bio-inspired computational methods have gained popularity recently. These methods mimic the seemingly complex behavior of organisms to tackle difficult and often overwhelming problems. For example, algorithms have been inspired by honeybees’ flight patterns when searching for nectar, ants’ social foraging strategies, the evasive murmurations of birds and fish, and even the growth patterns of slime molds. By modeling these natural processes mathematically, researchers can develop innovative solutions to complex challenges.Bio-inspired computational methods have gained popularity recently. These methods mimic the seemingly complex behavior of organisms to tackle difficult and often overwhelming problems. For example, algorithms have been inspired by honeybees’ flight patterns when searching for nectar, ants’ social foraging strategies, the evasive murmurations of birds and fish, and even the growth patterns of slime molds. By modeling these natural processes mathematically, researchers can develop innovative solutions to complex challenges.[#item_full_content]
A team of faculty and students from George Mason University recently discovered a vulnerability in a widely used anonymization tool. They presented their findings last week in Taiwan at the Association for Computing Machinery Conference on Computer and Communications Security (ACM CCS 2025). The paper is available on the arXiv preprint server.A team of faculty and students from George Mason University recently discovered a vulnerability in a widely used anonymization tool. They presented their findings last week in Taiwan at the Association for Computing Machinery Conference on Computer and Communications Security (ACM CCS 2025). The paper is available on the arXiv preprint server.[#item_full_content]