When artificial intelligence systems began acing long-standing academic assessments, researchers realized they had a problem: the tests were too easy. Popular evaluations, such as the Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU) exam, once considered formidable, are no longer challenging enough to meaningfully test advanced AI systems.When artificial intelligence systems began acing long-standing academic assessments, researchers realized they had a problem: the tests were too easy. Popular evaluations, such as the Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU) exam, once considered formidable, are no longer challenging enough to meaningfully test advanced AI systems.[#item_full_content]
Training police officers with a virtual-reality game can significantly improve their ability to regulate stress, even in realistic, high-pressure situations. The VR game, developed at the Donders Institute at Radboud University, has already been integrated into several police training programs.Training police officers with a virtual-reality game can significantly improve their ability to regulate stress, even in realistic, high-pressure situations. The VR game, developed at the Donders Institute at Radboud University, has already been integrated into several police training programs.[#item_full_content]
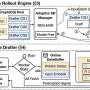
Reasoning large language models (LLMs) are designed to solve complex problems by breaking them down into a series of smaller steps. These powerful models are particularly good at challenging tasks like advanced programming and multistep planning. But developing reasoning models demands an enormous amount of computation and energy due to inefficiencies in the training process. While a few of the high-power processors continuously work through complicated queries, others in the group sit idle.Reasoning large language models (LLMs) are designed to solve complex problems by breaking them down into a series of smaller steps. These powerful models are particularly good at challenging tasks like advanced programming and multistep planning. But developing reasoning models demands an enormous amount of computation and energy due to inefficiencies in the training process. While a few of the high-power processors continuously work through complicated queries, others in the group sit idle.[#item_full_content]
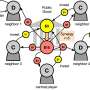
The Care Bears taught a generation of kids that sharing is caring, but not everyone has carried this principle into adulthood. Researchers at Michigan State University have found a new angle to promote cooperation: artificial intelligence (AI). The results of this study, titled “Promoting cooperation in the public goods game using artificial intelligent agents,” are published in npj Complexity.The Care Bears taught a generation of kids that sharing is caring, but not everyone has carried this principle into adulthood. Researchers at Michigan State University have found a new angle to promote cooperation: artificial intelligence (AI). The results of this study, titled “Promoting cooperation in the public goods game using artificial intelligent agents,” are published in npj Complexity.[#item_full_content]
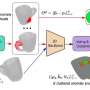
The automatic detection of surface-level irregularities—defects or anomalies—in 3D data is of significant interest for various real-world purposes, such as industrial quality inspection, infrastructure monitoring, robotics, and autonomous systems. However, collecting annotated defect examples at a large scale is costly, and existing 3D anomaly detection methods either require templates or heavy memory, multiple inference passes, and brittle heuristic clustering. These shortcomings limit real-life deployment.The automatic detection of surface-level irregularities—defects or anomalies—in 3D data is of significant interest for various real-world purposes, such as industrial quality inspection, infrastructure monitoring, robotics, and autonomous systems. However, collecting annotated defect examples at a large scale is costly, and existing 3D anomaly detection methods either require templates or heavy memory, multiple inference passes, and brittle heuristic clustering. These shortcomings limit real-life deployment.[#item_full_content]
When a human says an event is “probable” or “likely,” people generally have a shared, if fuzzy, understanding of what that means. But when an AI chatbot like ChatGPT uses the same word, it’s not assessing the odds the way we do, my colleagues and I found.When a human says an event is “probable” or “likely,” people generally have a shared, if fuzzy, understanding of what that means. But when an AI chatbot like ChatGPT uses the same word, it’s not assessing the odds the way we do, my colleagues and I found.[#item_full_content]
It is not easy to bring new technologies from the laboratory to market. Researchers and companies face very different demands for new developments and do not always find common ground. Scientists at Empa and other institutions have analyzed two emerging solar cell technologies to identify the greatest risks. Their conclusion: Research and industry must start collaborating much earlier.It is not easy to bring new technologies from the laboratory to market. Researchers and companies face very different demands for new developments and do not always find common ground. Scientists at Empa and other institutions have analyzed two emerging solar cell technologies to identify the greatest risks. Their conclusion: Research and industry must start collaborating much earlier.[#item_full_content]
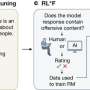
Large language models (LLMs) are dealing with an increasing amount of morally sensitive information as people turn to them for medical advice, companionship and therapy. However, they are not exactly known for possessing a moral compass.Large language models (LLMs) are dealing with an increasing amount of morally sensitive information as people turn to them for medical advice, companionship and therapy. However, they are not exactly known for possessing a moral compass.[#item_full_content]
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) agents, systems that learn to make predictions, generate content or tackle other tasks by analyzing large amounts of data, is becoming increasingly widespread. Some of these systems have become so advanced that they can also be combined in ways that allow them to interact with each other.The use of artificial intelligence (AI) agents, systems that learn to make predictions, generate content or tackle other tasks by analyzing large amounts of data, is becoming increasingly widespread. Some of these systems have become so advanced that they can also be combined in ways that allow them to interact with each other.[#item_full_content]
Just like each person has unique fingerprints, every CMOS chip has a distinctive “fingerprint” caused by tiny, random manufacturing variations. Engineers can leverage this unforgeable ID for authentication, to safeguard a device from attackers trying to steal private data.Just like each person has unique fingerprints, every CMOS chip has a distinctive “fingerprint” caused by tiny, random manufacturing variations. Engineers can leverage this unforgeable ID for authentication, to safeguard a device from attackers trying to steal private data.[#item_full_content]