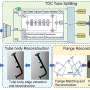
Complex tubes with flanges, joints and other components, characterized by a large number of diverse shapes and complex structures, are key parts of aircraft engines, rockets and other equipment. In order to ensure the smooth operation of this equipment, the dimensional accuracy of the tube must be ensured.Complex tubes with flanges, joints and other components, characterized by a large number of diverse shapes and complex structures, are key parts of aircraft engines, rockets and other equipment. In order to ensure the smooth operation of this equipment, the dimensional accuracy of the tube must be ensured.[#item_full_content]
As large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT continue to advance, user expectations of them keep growing, including with respect to how quickly they can respond to our increasingly intricate prompts requesting answers to ever-challenging problems and tasks.As large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT continue to advance, user expectations of them keep growing, including with respect to how quickly they can respond to our increasingly intricate prompts requesting answers to ever-challenging problems and tasks.[#item_full_content]
Let’s say you’re reading a story, or playing a game of chess. You may not have noticed, but each step of the way, your mind kept track of how the situation (or “state of the world”) was changing. You can imagine this as a sort of sequence of events list, which we use to update our prediction of what will happen next.Let’s say you’re reading a story, or playing a game of chess. You may not have noticed, but each step of the way, your mind kept track of how the situation (or “state of the world”) was changing. You can imagine this as a sort of sequence of events list, which we use to update our prediction of what will happen next.[#item_full_content]
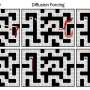
Diffusion models are widely used in many AI applications, but research on efficient inference-time scalability, particularly for reasoning and planning (known as System 2 abilities) has been lacking. In response, a research team has developed a new technology that enables high-performance and efficient inference for planning based on diffusion models.Diffusion models are widely used in many AI applications, but research on efficient inference-time scalability, particularly for reasoning and planning (known as System 2 abilities) has been lacking. In response, a research team has developed a new technology that enables high-performance and efficient inference for planning based on diffusion models.[#item_full_content]
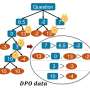
The Python package PhaseFieldX, developed by researcher Miguel Castillón at IMDEA Materials Institute, has been published in the Journal of Open Source Software (JOSS) in a paper titled “PhaseFieldX: An Open-Source Framework for Advanced Phase-Field Simulations.”The Python package PhaseFieldX, developed by researcher Miguel Castillón at IMDEA Materials Institute, has been published in the Journal of Open Source Software (JOSS) in a paper titled “PhaseFieldX: An Open-Source Framework for Advanced Phase-Field Simulations.”[#item_full_content]
Artificial intelligence is advancing at a dizzying speed. Like many new technologies, it offers significant benefits but also poses safety risks. Recognizing the potential dangers, leading researchers from Google DeepMind, OpenAI, Meta, Anthropic and a coalition of companies and nonprofit groups have come together to call for more to be done to monitor how AI systems “think.”Artificial intelligence is advancing at a dizzying speed. Like many new technologies, it offers significant benefits but also poses safety risks. Recognizing the potential dangers, leading researchers from Google DeepMind, OpenAI, Meta, Anthropic and a coalition of companies and nonprofit groups have come together to call for more to be done to monitor how AI systems “think.”[#item_full_content]
Large language models (LLMs) excel at using textual reasoning to understand the context of a document and provide a logical answer about its contents. But these same LLMs often struggle to correctly answer even the simplest math problems.Large language models (LLMs) excel at using textual reasoning to understand the context of a document and provide a logical answer about its contents. But these same LLMs often struggle to correctly answer even the simplest math problems.[#item_full_content]
Imagine a self-driving car navigating downtown traffic. To avoid a collision, it must judge whether the pedestrian at the corner is about to cross. Or consider an investment algorithm trading stocks—it needs to anticipate how human investors will react to news before making a move.Imagine a self-driving car navigating downtown traffic. To avoid a collision, it must judge whether the pedestrian at the corner is about to cross. Or consider an investment algorithm trading stocks—it needs to anticipate how human investors will react to news before making a move.[#item_full_content]
People have nicknamed the security system that monitors and controls internet traffic entering and leaving China “The Great Firewall of China.”People have nicknamed the security system that monitors and controls internet traffic entering and leaving China “The Great Firewall of China.”[#item_full_content]
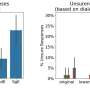
A new Cornell study has revealed that Amazon’s AI shopping assistant, Rufus, gives vague or incorrect responses to users writing in some English dialects, such as African American English (AAE), especially when prompts contain typos.A new Cornell study has revealed that Amazon’s AI shopping assistant, Rufus, gives vague or incorrect responses to users writing in some English dialects, such as African American English (AAE), especially when prompts contain typos.[#item_full_content]