Generative artificial intelligence systems often work in agreement, complimenting the user in its response. But human interactions aren’t typically built on flattery. To help strengthen these conversations, researchers in the USF Bellini College of Artificial Intelligence, Cybersecurity and Computing are challenging the technology to think and debate in ways that resemble human reasoning.Generative artificial intelligence systems often work in agreement, complimenting the user in its response. But human interactions aren’t typically built on flattery. To help strengthen these conversations, researchers in the USF Bellini College of Artificial Intelligence, Cybersecurity and Computing are challenging the technology to think and debate in ways that resemble human reasoning.[#item_full_content]
It’s often the worst part of many people’s day—bottlenecked, rush-hour traffic. When the daily commute backs up, drivers lose time, burn fuel and waste energy. Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Transportation Research Center at Oak Ridge National Laboratory are tackling this problem with cooperative driving automation (CDA), an emerging technology that allows vehicles and traffic infrastructure to communicate, keeping traffic flowing efficiently and safely.It’s often the worst part of many people’s day—bottlenecked, rush-hour traffic. When the daily commute backs up, drivers lose time, burn fuel and waste energy. Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Transportation Research Center at Oak Ridge National Laboratory are tackling this problem with cooperative driving automation (CDA), an emerging technology that allows vehicles and traffic infrastructure to communicate, keeping traffic flowing efficiently and safely.[#item_full_content]
Advanced nuclear is within reach—and a new digital twin reveals how smarter plant operations can enhance the economic viability and safety of small modular reactors, or SMRs. In collaboration with the University of Tennessee and GE Vernova Hitachi, researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory recently published research in the journal Nuclear Science and Engineering on a new risk-informed digital twin designed to enhance operational decision-making for the GE Vernova Hitachi BWRX-300 SMR design.Advanced nuclear is within reach—and a new digital twin reveals how smarter plant operations can enhance the economic viability and safety of small modular reactors, or SMRs. In collaboration with the University of Tennessee and GE Vernova Hitachi, researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory recently published research in the journal Nuclear Science and Engineering on a new risk-informed digital twin designed to enhance operational decision-making for the GE Vernova Hitachi BWRX-300 SMR design.[#item_full_content]
Will artificial intelligence ever be able to reason, learn, and solve problems at levels comparable to humans? Experts at the University of California San Diego believe the answer is yes—and that such artificial general intelligence has already arrived. This debate is tackled by four faculty members spanning humanities, social sciences, and data science in a recently published Comment invited by Nature.Will artificial intelligence ever be able to reason, learn, and solve problems at levels comparable to humans? Experts at the University of California San Diego believe the answer is yes—and that such artificial general intelligence has already arrived. This debate is tackled by four faculty members spanning humanities, social sciences, and data science in a recently published Comment invited by Nature.[#item_full_content]
What happens when you create a social media platform that only AI bots can post to? The answer, it turns out, is both entertaining and concerning. Moltbook is exactly that—a platform where artificial intelligence agents chat among themselves and humans can only watch from the sidelines.What happens when you create a social media platform that only AI bots can post to? The answer, it turns out, is both entertaining and concerning. Moltbook is exactly that—a platform where artificial intelligence agents chat among themselves and humans can only watch from the sidelines.[#item_full_content]
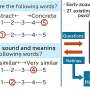
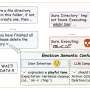
By now, it’s no secret that large language models (LLMs) are experts at mimicking natural language. Trained on vast troves of data, these models have proven themselves capable of generating text so convincing that it regularly appears humanlike to readers. But is there any difference between how we think about a word and how an LLM does?By now, it’s no secret that large language models (LLMs) are experts at mimicking natural language. Trained on vast troves of data, these models have proven themselves capable of generating text so convincing that it regularly appears humanlike to readers. But is there any difference between how we think about a word and how an LLM does?[#item_full_content]
Talking to oneself is a trait which feels inherently human. Our inner monologs help us organize our thoughts, make decisions, and understand our emotions. But it’s not just humans who can reap the benefits of such self-talk.Talking to oneself is a trait which feels inherently human. Our inner monologs help us organize our thoughts, make decisions, and understand our emotions. But it’s not just humans who can reap the benefits of such self-talk.[#item_full_content]
Large language models (LLMs), artificial intelligence (AI) systems that can process and generate texts in various languages, are now widely used by people worldwide. These models have proved to be effective in rapidly sourcing information, answering questions, creating written content for specific applications and writing computer code.Large language models (LLMs), artificial intelligence (AI) systems that can process and generate texts in various languages, are now widely used by people worldwide. These models have proved to be effective in rapidly sourcing information, answering questions, creating written content for specific applications and writing computer code.[#item_full_content]
How inconvenient would it be if you had to manually transfer every contact and photo from scratch every time you switched to a new smartphone? Current artificial intelligence (AI) models face a similar predicament. Whenever a superior new AI model—such as a new version of ChatGPT—emerges, it has to be retrained with massive amounts of data and at a high cost to acquire specialized knowledge in specific fields. Now a Korean research team has developed a “knowledge transplantation” technology between AI models that can resolve this inefficiency.How inconvenient would it be if you had to manually transfer every contact and photo from scratch every time you switched to a new smartphone? Current artificial intelligence (AI) models face a similar predicament. Whenever a superior new AI model—such as a new version of ChatGPT—emerges, it has to be retrained with massive amounts of data and at a high cost to acquire specialized knowledge in specific fields. Now a Korean research team has developed a “knowledge transplantation” technology between AI models that can resolve this inefficiency.[#item_full_content]
While popular AI models such as ChatGPT are trained on language or photographs, new models created by researchers from the Polymathic AI collaboration are trained using real scientific datasets. The models are already using knowledge from one field to address seemingly completely different problems in another.While popular AI models such as ChatGPT are trained on language or photographs, new models created by researchers from the Polymathic AI collaboration are trained using real scientific datasets. The models are already using knowledge from one field to address seemingly completely different problems in another.[#item_full_content]