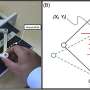
Haptic feedback stands as a cornerstone for the authenticity and depth of engagement in virtual reality and teleoperation systems. Yet, existing haptic devices have grappled with the fidelity of replicating tactile properties, hindered by the constraints on their degrees of freedom and expressive range. This limitation has ignited an urgent quest for innovative solutions that can augment the responsiveness and adaptability of haptic systems.Haptic feedback stands as a cornerstone for the authenticity and depth of engagement in virtual reality and teleoperation systems. Yet, existing haptic devices have grappled with the fidelity of replicating tactile properties, hindered by the constraints on their degrees of freedom and expressive range. This limitation has ignited an urgent quest for innovative solutions that can augment the responsiveness and adaptability of haptic systems.[#item_full_content]
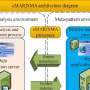
A recent study introduces MARISMA, a new framework developed to address limitations in existing risk analysis models for cybersecurity. The study conducted by Prof. Antonio Santos-Olmo and his team identifies 10 major weaknesses in current models, leading to the development of MARISMA.A recent study introduces MARISMA, a new framework developed to address limitations in existing risk analysis models for cybersecurity. The study conducted by Prof. Antonio Santos-Olmo and his team identifies 10 major weaknesses in current models, leading to the development of MARISMA.[#item_full_content]
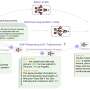
A team of AI researchers at the Chinese technology company Baidu Inc. is proposing a new reasoning framework designed to improve the reliability and traceability of LLMs. The group has published a paper describing their ideas on the arXiv preprint server.A team of AI researchers at the Chinese technology company Baidu Inc. is proposing a new reasoning framework designed to improve the reliability and traceability of LLMs. The group has published a paper describing their ideas on the arXiv preprint server.[#item_full_content]
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) models like OpenAI’s GPT-4o or Stability AI’s Stable Diffusion are surprisingly capable at creating new text, code, images and videos. Training them, however, requires such vast amounts of data that developers are already running up against supply limitations and may soon exhaust training resources altogether.Generative artificial intelligence (AI) models like OpenAI’s GPT-4o or Stability AI’s Stable Diffusion are surprisingly capable at creating new text, code, images and videos. Training them, however, requires such vast amounts of data that developers are already running up against supply limitations and may soon exhaust training resources altogether.[#item_full_content]
Our insatiable demand for digital content and services has been driving a rise in energy-hungry data centers.Our insatiable demand for digital content and services has been driving a rise in energy-hungry data centers.[#item_full_content]
A new study from SUNY Polytechnic Institute provides a detailed overview of deepfake datasets and identifies key challenges, offering valuable insights for researchers, engineers, and practitioners. It emphasizes the importance of developing proactive detection methods and improving existing datasets to combat deepfake threats effectively.A new study from SUNY Polytechnic Institute provides a detailed overview of deepfake datasets and identifies key challenges, offering valuable insights for researchers, engineers, and practitioners. It emphasizes the importance of developing proactive detection methods and improving existing datasets to combat deepfake threats effectively.[#item_full_content]
An algorithm developed by Washington State University researchers can better find data anomalies than current anomaly-detection software, including in streaming data.An algorithm developed by Washington State University researchers can better find data anomalies than current anomaly-detection software, including in streaming data.[#item_full_content]
Computer science researchers have developed a new method for predicting what data wireless computing users will need before they need it, making wireless networks faster and more reliable. The new method makes use of a technique called a “digital twin,” which effectively clones the network it is supporting.Computer science researchers have developed a new method for predicting what data wireless computing users will need before they need it, making wireless networks faster and more reliable. The new method makes use of a technique called a “digital twin,” which effectively clones the network it is supporting.[#item_full_content]
Organizations are increasingly utilizing machine-learning models to allocate scarce resources or opportunities. For instance, such models can help companies screen resumes to choose job interview candidates or aid hospitals in ranking kidney transplant patients based on their likelihood of survival.Organizations are increasingly utilizing machine-learning models to allocate scarce resources or opportunities. For instance, such models can help companies screen resumes to choose job interview candidates or aid hospitals in ranking kidney transplant patients based on their likelihood of survival.[#item_full_content]
As artificial intelligence models become increasingly prevalent and are integrated into diverse sectors like health care, finance, education, transportation, and entertainment, understanding how they work under the hood is critical. Interpreting the mechanisms underlying AI models enables us to audit them for safety and biases, with the potential to deepen our understanding of the science behind intelligence itself.As artificial intelligence models become increasingly prevalent and are integrated into diverse sectors like health care, finance, education, transportation, and entertainment, understanding how they work under the hood is critical. Interpreting the mechanisms underlying AI models enables us to audit them for safety and biases, with the potential to deepen our understanding of the science behind intelligence itself.[#item_full_content]