Computer-aided design (CAD) systems are tried-and-true tools used to design many of the physical objects we use each day. But CAD software requires extensive expertise to master, and many tools incorporate such a high level of detail they don’t lend themselves to brainstorming or rapid prototyping.Computer-aided design (CAD) systems are tried-and-true tools used to design many of the physical objects we use each day. But CAD software requires extensive expertise to master, and many tools incorporate such a high level of detail they don’t lend themselves to brainstorming or rapid prototyping.Robotics[#item_full_content]
When scientists test algorithms that sort or classify data, they often turn to a trusted tool called Normalized Mutual Information (or NMI) to measure how well an algorithm’s output matches reality. But according to new research, that tool may not be as reliable as many assume.When scientists test algorithms that sort or classify data, they often turn to a trusted tool called Normalized Mutual Information (or NMI) to measure how well an algorithm’s output matches reality. But according to new research, that tool may not be as reliable as many assume.Computer Sciences[#item_full_content]
When scientists test algorithms that sort or classify data, they often turn to a trusted tool called Normalized Mutual Information (or NMI) to measure how well an algorithm’s output matches reality. But according to new research, that tool may not be as reliable as many assume.When scientists test algorithms that sort or classify data, they often turn to a trusted tool called Normalized Mutual Information (or NMI) to measure how well an algorithm’s output matches reality. But according to new research, that tool may not be as reliable as many assume.[#item_full_content]
Does the latest track by your favorite singer sound slightly off? You may be right. Fraudulent AI-generated tracks are increasingly appearing in artists’ own profiles on streaming platforms, presented as their original work.Does the latest track by your favorite singer sound slightly off? You may be right. Fraudulent AI-generated tracks are increasingly appearing in artists’ own profiles on streaming platforms, presented as their original work.Machine learning & AI[#item_full_content]
Three years after ChatGPT made OpenAI the leader in artificial intelligence and a household name, rivals have closed the gap and some investors are wondering if the sensation has the wherewithal to stay dominant.Three years after ChatGPT made OpenAI the leader in artificial intelligence and a household name, rivals have closed the gap and some investors are wondering if the sensation has the wherewithal to stay dominant.Business[#item_full_content]
EPFL researchers have developed new software—now spun-off into a start-up—that eliminates the need for data to be sent to third-party cloud services when AI is used to complete a task. This could challenge the business model of Big Tech.EPFL researchers have developed new software—now spun-off into a start-up—that eliminates the need for data to be sent to third-party cloud services when AI is used to complete a task. This could challenge the business model of Big Tech.Software[#item_full_content]
The new TikTok trend “AI homeless man prank” has sparked a wave of outrage and police responses in the United States and beyond. The prank involves using AI image generators to create realistic photos depicting fake homeless people appearing to be at someone’s door or inside their home.The new TikTok trend “AI homeless man prank” has sparked a wave of outrage and police responses in the United States and beyond. The prank involves using AI image generators to create realistic photos depicting fake homeless people appearing to be at someone’s door or inside their home.Machine learning & AI[#item_full_content]
President Donald Trump signed an executive order on Dec. 11, 2025, that aims to supersede state-level artificial intelligence laws that the administration views as a hindrance to innovation in AI.President Donald Trump signed an executive order on Dec. 11, 2025, that aims to supersede state-level artificial intelligence laws that the administration views as a hindrance to innovation in AI.Business[#item_full_content]
Which headline are you more likely to click on?Which headline are you more likely to click on?Machine learning & AI[#item_full_content]
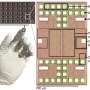
Robots small enough to travel autonomously through the human body to repair damaged sites may seem the stuff of science fiction dreams. But this vision of surgery on a microscale is a step closer to reality, with news that researchers from the University of Pennsylvania and the University of Michigan have built a robot smaller than a millimeter that has an onboard computer and sensors.Robots small enough to travel autonomously through the human body to repair damaged sites may seem the stuff of science fiction dreams. But this vision of surgery on a microscale is a step closer to reality, with news that researchers from the University of Pennsylvania and the University of Michigan have built a robot smaller than a millimeter that has an onboard computer and sensors.[#item_full_content]