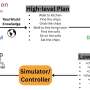
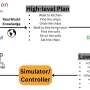
When it comes to training robots to perform agile, single-task motor skills, such as handstands or backflips, artificial intelligence methods can be very useful. But if you want to train your robot to perform multiple tasks—say, performing a backward flip into a handstand—things get a little more complicated.When it comes to training robots to perform agile, single-task motor skills, such as handstands or backflips, artificial intelligence methods can be very useful. But if you want to train your robot to perform multiple tasks—say, performing a backward flip into a handstand—things get a little more complicated.[#item_full_content]
When it comes to training robots to perform agile, single-task motor skills, such as handstands or backflips, artificial intelligence methods can be very useful. But if you want to train your robot to perform multiple tasks—say, performing a backward flip into a handstand—things get a little more complicated.When it comes to training robots to perform agile, single-task motor skills, such as handstands or backflips, artificial intelligence methods can be very useful. But if you want to train your robot to perform multiple tasks—say, performing a backward flip into a handstand—things get a little more complicated.Robotics[#item_full_content]
When the FORTRAN programming language debuted in 1957, it transformed how scientists and engineers programmed computers. Complex calculations could suddenly be expressed in concise, math-like notation using arrays—collections of values that make it easier to describe operations on data. That simple idea evolved into today’s “tensors,” which power many of the world’s most advanced AI and scientific computing systems through modern frameworks like NumPy and PyTorch.When the FORTRAN programming language debuted in 1957, it transformed how scientists and engineers programmed computers. Complex calculations could suddenly be expressed in concise, math-like notation using arrays—collections of values that make it easier to describe operations on data. That simple idea evolved into today’s “tensors,” which power many of the world’s most advanced AI and scientific computing systems through modern frameworks like NumPy and PyTorch.[#item_full_content]
Large language models (LLMs), such as the model underpinning the functioning of OpenAI’s platform ChatGPT, are now widely used to tackle a wide range of tasks, ranging from sourcing information to the generation of texts in different languages and even code. Many scientists and engineers also started using these models to conduct research or advance other technologies.Large language models (LLMs), such as the model underpinning the functioning of OpenAI’s platform ChatGPT, are now widely used to tackle a wide range of tasks, ranging from sourcing information to the generation of texts in different languages and even code. Many scientists and engineers also started using these models to conduct research or advance other technologies.[#item_full_content]
Large language models (LLMs), such as the model underpinning the functioning of OpenAI’s platform ChatGPT, are now widely used to tackle a wide range of tasks, ranging from sourcing information to the generation of texts in different languages and even code. Many scientists and engineers also started using these models to conduct research or advance other technologies.Large language models (LLMs), such as the model underpinning the functioning of OpenAI’s platform ChatGPT, are now widely used to tackle a wide range of tasks, ranging from sourcing information to the generation of texts in different languages and even code. Many scientists and engineers also started using these models to conduct research or advance other technologies.Robotics[#item_full_content]
Researchers from Saarland University and the Max Planck Institute for Software Systems have, for the first time, shown that the reactions of humans and large language models (LLMs) to complex or misleading program code significantly align, by comparing brain activity of study participants with model uncertainty.Researchers from Saarland University and the Max Planck Institute for Software Systems have, for the first time, shown that the reactions of humans and large language models (LLMs) to complex or misleading program code significantly align, by comparing brain activity of study participants with model uncertainty.Computer Sciences[#item_full_content]
Researchers from Saarland University and the Max Planck Institute for Software Systems have, for the first time, shown that the reactions of humans and large language models (LLMs) to complex or misleading program code significantly align, by comparing brain activity of study participants with model uncertainty.Researchers from Saarland University and the Max Planck Institute for Software Systems have, for the first time, shown that the reactions of humans and large language models (LLMs) to complex or misleading program code significantly align, by comparing brain activity of study participants with model uncertainty.[#item_full_content]
Dell Technologies Inc., HP Inc. and other tech companies are warning of potential memory-chip supply shortages in the coming year due to soaring demand from the build-out of artificial intelligence infrastructure.Dell Technologies Inc., HP Inc. and other tech companies are warning of potential memory-chip supply shortages in the coming year due to soaring demand from the build-out of artificial intelligence infrastructure.Electronics & Semiconductors[#item_full_content]
A dystopian future where advanced artificial intelligence (AI) systems replace human decision-making has long been a trope of science fiction. The malevolent computer HAL, which takes control of the spaceship in Stanley Kubrick’s film, 2001: A Space Odyssey, is a chilling example.A dystopian future where advanced artificial intelligence (AI) systems replace human decision-making has long been a trope of science fiction. The malevolent computer HAL, which takes control of the spaceship in Stanley Kubrick’s film, 2001: A Space Odyssey, is a chilling example.Software[#item_full_content]
Large language models (LLMs), such as the model underpinning the functioning of OpenAI’s conversational platform ChatGPT, have proved to perform well on various language-related and coding tasks. Some computer scientists have recently been exploring the possibility that these models could also be used by malicious users and hackers to plan cyber-attacks or access people’s personal data.Large language models (LLMs), such as the model underpinning the functioning of OpenAI’s conversational platform ChatGPT, have proved to perform well on various language-related and coding tasks. Some computer scientists have recently been exploring the possibility that these models could also be used by malicious users and hackers to plan cyber-attacks or access people’s personal data.Security[#item_full_content]