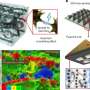
Current vision systems for robots and drones rely on 3D sensors that, although powerful, do not always keep up with the fast-paced, unpredictable movement of the real world. These systems often struggle to measure speed instantly or are too bulky and expensive for everyday use. Now, in a paper published in the journal Nature, scientists report how they have developed a 4D imaging sensor on a chip that creates 3D maps of an environment while simultaneously tracking the speed of moving objects.Current vision systems for robots and drones rely on 3D sensors that, although powerful, do not always keep up with the fast-paced, unpredictable movement of the real world. These systems often struggle to measure speed instantly or are too bulky and expensive for everyday use. Now, in a paper published in the journal Nature, scientists report how they have developed a 4D imaging sensor on a chip that creates 3D maps of an environment while simultaneously tracking the speed of moving objects.[#item_full_content]
Whether in the kitchen or on a workshop floor, robot assistants that can fetch items for people could be extremely useful. Now, a team of Brown University researchers has developed a way of making robots better at figuring out exactly which items a user might want them to retrieve.Whether in the kitchen or on a workshop floor, robot assistants that can fetch items for people could be extremely useful. Now, a team of Brown University researchers has developed a way of making robots better at figuring out exactly which items a user might want them to retrieve.[#item_full_content]
A robot that can locate lost items on command, the latest development at the Technical University of Munich (TUM), combines knowledge from the internet with a spatial map of its surroundings to efficiently find the objects being sought. The new robot from Prof. Angela Schoellig’s TUM Learning Systems and Robotics Lab looks like a broomstick on wheels with a camera mounted at the top. It is one of the first robots that not only integrates image understanding but also applies it to a clearly defined task.A robot that can locate lost items on command, the latest development at the Technical University of Munich (TUM), combines knowledge from the internet with a spatial map of its surroundings to efficiently find the objects being sought. The new robot from Prof. Angela Schoellig’s TUM Learning Systems and Robotics Lab looks like a broomstick on wheels with a camera mounted at the top. It is one of the first robots that not only integrates image understanding but also applies it to a clearly defined task.[#item_full_content]
Experienced human cyclists can perform a wide range of maneuvers and acrobatics while riding their bicycle, from balancing in place to riding on a single wheel or hopping over obstacles. Reproducing these agile maneuvers in two-wheeled robots could open new opportunities both for entertainment or robot sports and for the completion of complex missions in rough terrain.Experienced human cyclists can perform a wide range of maneuvers and acrobatics while riding their bicycle, from balancing in place to riding on a single wheel or hopping over obstacles. Reproducing these agile maneuvers in two-wheeled robots could open new opportunities both for entertainment or robot sports and for the completion of complex missions in rough terrain.[#item_full_content]
MIT researchers have developed a generative artificial intelligence-driven approach for planning long-term visual tasks, like robot navigation, that is about twice as effective as some existing techniques. Their method uses a specialized vision-language model to perceive the scenario in an image and simulate actions needed to reach a goal. Then a second model translates those simulations into a standard programming language for planning problems, and refines the solution.MIT researchers have developed a generative artificial intelligence-driven approach for planning long-term visual tasks, like robot navigation, that is about twice as effective as some existing techniques. Their method uses a specialized vision-language model to perceive the scenario in an image and simulate actions needed to reach a goal. Then a second model translates those simulations into a standard programming language for planning problems, and refines the solution.[#item_full_content]
A new type of robotic hand developed at The University of Texas at Austin demonstrates such sensitive touch that it can grasp objects as fragile as a potato chip or a raspberry without crushing them. The technology, called Fragile Object Grasping with Tactile Sensing (FORTE), combines advanced tactile sensing with soft robotics. The breakthrough could improve robot performance when a light touch is needed, such as in health care and manufacturing.A new type of robotic hand developed at The University of Texas at Austin demonstrates such sensitive touch that it can grasp objects as fragile as a potato chip or a raspberry without crushing them. The technology, called Fragile Object Grasping with Tactile Sensing (FORTE), combines advanced tactile sensing with soft robotics. The breakthrough could improve robot performance when a light touch is needed, such as in health care and manufacturing.[#item_full_content]
RMIT University engineers in Australia have built a remote-controlled minibot that hoovers up oil spills using an innovative filtering system inspired by sea urchins. Oil spills are still a serious problem around the world. They can badly damage oceans and coasts, kill or injure sea animals and birds, and cost billions of dollars to clean up and repair the damage.RMIT University engineers in Australia have built a remote-controlled minibot that hoovers up oil spills using an innovative filtering system inspired by sea urchins. Oil spills are still a serious problem around the world. They can badly damage oceans and coasts, kill or injure sea animals and birds, and cost billions of dollars to clean up and repair the damage.[#item_full_content]
Engineers at Oxford University have developed a rapid, ultra-low-cost method for manufacturing soft robots using common lab equipment. The method has been published in Advanced Science. The new technique enables researchers to fabricate soft robotic actuators—the flexible components that power movement—in under 10 minutes at a material cost of less than $0.10 (US Dollars) per unit.Engineers at Oxford University have developed a rapid, ultra-low-cost method for manufacturing soft robots using common lab equipment. The method has been published in Advanced Science. The new technique enables researchers to fabricate soft robotic actuators—the flexible components that power movement—in under 10 minutes at a material cost of less than $0.10 (US Dollars) per unit.[#item_full_content]
Robots are becoming increasingly capable in vision and movement, yet touch remains one of their major weaknesses. Now, researchers have developed a miniature tactile sensor that could give robots something much closer to a human sense of touch.Robots are becoming increasingly capable in vision and movement, yet touch remains one of their major weaknesses. Now, researchers have developed a miniature tactile sensor that could give robots something much closer to a human sense of touch.[#item_full_content]
Humanoid robots, robotic systems with a human-like body structure, have the potential of tackling various real-world tasks that are currently being completed by humans. In recent years, many robotics researchers and computer scientists have been trying to broaden these robots’ capabilities and improve how they move in their surroundings.Humanoid robots, robotic systems with a human-like body structure, have the potential of tackling various real-world tasks that are currently being completed by humans. In recent years, many robotics researchers and computer scientists have been trying to broaden these robots’ capabilities and improve how they move in their surroundings.[#item_full_content]