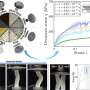
Rice becomes weaker when compressed quickly, while staying stronger under slow pressure—a discovery enabling scientists to design a new material that could be used to build “soft” robots that change stiffness automatically and protective gear that adapts to impact speed. Researchers harnessed this effect to design a new “metamaterial”—an artificially engineered composite structure designed to behave in ways impossible for natural materials.Rice becomes weaker when compressed quickly, while staying stronger under slow pressure—a discovery enabling scientists to design a new material that could be used to build “soft” robots that change stiffness automatically and protective gear that adapts to impact speed. Researchers harnessed this effect to design a new “metamaterial”—an artificially engineered composite structure designed to behave in ways impossible for natural materials.[#item_full_content]
A leading cause of disability in the United States is hemiparesis, a condition where impaired motor control, muscle weakness, and spasticity affect one side of the body. Occurring in 80% of stroke survivors, reduced mobility and decreased quality of life are challenges that impact millions of individuals.A leading cause of disability in the United States is hemiparesis, a condition where impaired motor control, muscle weakness, and spasticity affect one side of the body. Occurring in 80% of stroke survivors, reduced mobility and decreased quality of life are challenges that impact millions of individuals.[#item_full_content]
Eyes are said to be the mirror of the soul. Eyes and gaze direction guide attention, evoke emotions and activate the brain’s social perception mechanisms. Researchers at Tampere University and the University of Bremen conducted a study examining how people perceive the minds of humanoid robots. Mind perception refers to the way humans detect and infer that other people, beings or even objects possess consciousness, emotions and cognitive states.Eyes are said to be the mirror of the soul. Eyes and gaze direction guide attention, evoke emotions and activate the brain’s social perception mechanisms. Researchers at Tampere University and the University of Bremen conducted a study examining how people perceive the minds of humanoid robots. Mind perception refers to the way humans detect and infer that other people, beings or even objects possess consciousness, emotions and cognitive states.[#item_full_content]
While the statement, “Humanoid robots are coming,” might cause anxiety for some, for one Georgia Tech research team, working with humanlike robots couldn’t be more exciting. The researchers have developed a new “thinking” technology for two-legged robots, increasing their balance and agility.While the statement, “Humanoid robots are coming,” might cause anxiety for some, for one Georgia Tech research team, working with humanlike robots couldn’t be more exciting. The researchers have developed a new “thinking” technology for two-legged robots, increasing their balance and agility.[#item_full_content]
Mobile robots must continuously estimate their position to navigate autonomously. However, satellite-based navigation systems are not always reliable: signals may degrade near buildings or become unavailable indoors. To operate safely and efficiently, robots must interpret their surroundings using onboard sensors and robust localization algorithms.Mobile robots must continuously estimate their position to navigate autonomously. However, satellite-based navigation systems are not always reliable: signals may degrade near buildings or become unavailable indoors. To operate safely and efficiently, robots must interpret their surroundings using onboard sensors and robust localization algorithms.[#item_full_content]
Human hands are a wonder of nature and unmatched in the animal kingdom. They can twist caps, flick switches, handle tiny objects with ease, and perform thousands of tasks every day. Robot hands struggle to keep up. They typically miss the sense of touch, can’t move many fingers at once, and lose track of what they are holding when their fingers block their camera’s view. Scientists have now developed a smarter way to train a robot’s brain to give its hands human-like dexterity.Human hands are a wonder of nature and unmatched in the animal kingdom. They can twist caps, flick switches, handle tiny objects with ease, and perform thousands of tasks every day. Robot hands struggle to keep up. They typically miss the sense of touch, can’t move many fingers at once, and lose track of what they are holding when their fingers block their camera’s view. Scientists have now developed a smarter way to train a robot’s brain to give its hands human-like dexterity.[#item_full_content]
The compound eyes of the humble fruit fly are a marvel of nature. They are wide-angle and can process visual information several times faster than the human eye. Inspired by this biological masterpiece, researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed an insect-scale compound eye that can both see and smell, potentially improving how drones and robots navigate complex environments and avoid obstacles.The compound eyes of the humble fruit fly are a marvel of nature. They are wide-angle and can process visual information several times faster than the human eye. Inspired by this biological masterpiece, researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed an insect-scale compound eye that can both see and smell, potentially improving how drones and robots navigate complex environments and avoid obstacles.[#item_full_content]
EPFL roboticists have shown that when a modular robot shares power, sensing, and communication resources among its individual units, it is significantly more resistant to failure than traditional robotic systems, where the breakdown of one element often means a loss of functionality.EPFL roboticists have shown that when a modular robot shares power, sensing, and communication resources among its individual units, it is significantly more resistant to failure than traditional robotic systems, where the breakdown of one element often means a loss of functionality.[#item_full_content]
Penn Engineers have developed a system that lets robots see around corners using radio waves processed by AI, a capability that could improve the safety and performance of driverless cars as well as robots operating in cluttered indoor settings like warehouses and factories.Penn Engineers have developed a system that lets robots see around corners using radio waves processed by AI, a capability that could improve the safety and performance of driverless cars as well as robots operating in cluttered indoor settings like warehouses and factories.[#item_full_content]
Soft robots made out of flexible, biocompatible materials are in high demand in industries from health care to manufacturing, but precisely designing and controlling such robots for specific purposes is a perennial challenge. What if you could 3D print a soft robot with predictable shape-morphing capabilities already built in? Harvard 3D printing experts have shown it’s possible.Soft robots made out of flexible, biocompatible materials are in high demand in industries from health care to manufacturing, but precisely designing and controlling such robots for specific purposes is a perennial challenge. What if you could 3D print a soft robot with predictable shape-morphing capabilities already built in? Harvard 3D printing experts have shown it’s possible.[#item_full_content]