The use of artificial intelligence (AI) systems, such as the models underpinning the functioning of ChatGPT and various other online platforms, has grown exponentially over the past few years. Current hardware and electronic devices, however, might not be best suited for running these systems, which are computationally intensive and can drain huge amounts of energy.The use of artificial intelligence (AI) systems, such as the models underpinning the functioning of ChatGPT and various other online platforms, has grown exponentially over the past few years. Current hardware and electronic devices, however, might not be best suited for running these systems, which are computationally intensive and can drain huge amounts of energy.Hardware[#item_full_content]
How do you translate ancient Palmyrene script from a Roman tombstone? How many paired tendons are supported by a specific sesamoid bone in a hummingbird? Can you identify closed syllables in Biblical Hebrew based on the latest scholarship on Tiberian pronunciation traditions?How do you translate ancient Palmyrene script from a Roman tombstone? How many paired tendons are supported by a specific sesamoid bone in a hummingbird? Can you identify closed syllables in Biblical Hebrew based on the latest scholarship on Tiberian pronunciation traditions?Machine learning & AI[#item_full_content]
Amazon.com Inc. is in talks to invest as much as $50 billion in OpenAI and expand an agreement that involves selling computer power to the AI startup, according to a person with knowledge of the matter. OpenAI is also weighing a deal in which Amazon would use the startup’s artificial intelligence models, which power the popular ChatGPT chatbot, in its products and platforms, the person said. Amazon’s employees could also access the model for their work.Amazon.com Inc. is in talks to invest as much as $50 billion in OpenAI and expand an agreement that involves selling computer power to the AI startup, according to a person with knowledge of the matter. OpenAI is also weighing a deal in which Amazon would use the startup’s artificial intelligence models, which power the popular ChatGPT chatbot, in its products and platforms, the person said. Amazon’s employees could also access the model for their work.Business[#item_full_content]
AI can help displaced people avoid exploitation, but humans must call the shots, warn experts. For Susan Achiech, life began in Kenya’s Kakuma refugee camp, where her South Sudanese parents fled to for safety in the early 1990s. Now 26, she lives in Canada, running her own gaming company, Tech Femme Algorithms, while working as an insurance advisor and studying gaming programming.AI can help displaced people avoid exploitation, but humans must call the shots, warn experts. For Susan Achiech, life began in Kenya’s Kakuma refugee camp, where her South Sudanese parents fled to for safety in the early 1990s. Now 26, she lives in Canada, running her own gaming company, Tech Femme Algorithms, while working as an insurance advisor and studying gaming programming.Business[#item_full_content]
When it comes to powering aircraft, jet engines need dense, energy-packed fuels. Right now, nearly all of that fuel comes from petroleum, as batteries don’t yet deliver enough punch for most flights. Scientists have long dreamed of a synthetic alternative: teaching microbes to ferment plant material into high-performance jet fuels. But designing these microbial “mini-factories” has traditionally been slow and expensive because of the unpredictability of biological systems.When it comes to powering aircraft, jet engines need dense, energy-packed fuels. Right now, nearly all of that fuel comes from petroleum, as batteries don’t yet deliver enough punch for most flights. Scientists have long dreamed of a synthetic alternative: teaching microbes to ferment plant material into high-performance jet fuels. But designing these microbial “mini-factories” has traditionally been slow and expensive because of the unpredictability of biological systems.Energy & Green Tech[#item_full_content]
Achieving high reliability in AI systems—such as autonomous vehicles that stay on course even in snowstorms or medical AI that can diagnose cancer from low-resolution images—depends heavily on model robustness. While data augmentation has long been a go-to technique for enhancing this robustness, the specific conditions under which it works best remained unclear—until now.Achieving high reliability in AI systems—such as autonomous vehicles that stay on course even in snowstorms or medical AI that can diagnose cancer from low-resolution images—depends heavily on model robustness. While data augmentation has long been a go-to technique for enhancing this robustness, the specific conditions under which it works best remained unclear—until now.Machine learning & AI[#item_full_content]
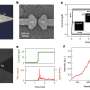
The promise of smart wearables is often talked up, and while there have been some impressive innovations, we are still not seeing their full potential. Among the things holding them back is that the chips that operate them are stiff, brittle, and power-hungry. To overcome these problems, researchers from Tsinghua University and Peking University in China have developed FLEXI, a new family of flexible chips. They are thinner than a human hair, flexible enough to be folded thousands of times, and incorporate AI.The promise of smart wearables is often talked up, and while there have been some impressive innovations, we are still not seeing their full potential. Among the things holding them back is that the chips that operate them are stiff, brittle, and power-hungry. To overcome these problems, researchers from Tsinghua University and Peking University in China have developed FLEXI, a new family of flexible chips. They are thinner than a human hair, flexible enough to be folded thousands of times, and incorporate AI.Electronics & Semiconductors[#item_full_content]
Federal and state governments have outlawed “revenge porn,” the nonconsensual online sharing of sexual images of individuals, often by former partners. Last year, South Carolina became the 50th state to enact such a law. The recent rise of easy-to-use generative AI tools, however, has introduced a new wrinkle: What happens when those images look real but have been created by AI? What’s lawful in the U.S. and who’s responsible is not yet clear.Federal and state governments have outlawed “revenge porn,” the nonconsensual online sharing of sexual images of individuals, often by former partners. Last year, South Carolina became the 50th state to enact such a law. The recent rise of easy-to-use generative AI tools, however, has introduced a new wrinkle: What happens when those images look real but have been created by AI? What’s lawful in the U.S. and who’s responsible is not yet clear.Business[#item_full_content]
Meta Platforms Inc.’s better-than-expected sales outlook helped ease Wall Street concerns about plans for unprecedented spending on artificial intelligence this year. The social networking giant topped projections for holiday quarter revenue and gave a strong forecast for the current period during its earnings report on Jan. 28. Improvements in its online advertising business are making it possible for Meta to spend hundreds of billions of dollars over the next few years on AI infrastructure. Meta’s shares jumped more than 11% in extended trading.Meta Platforms Inc.’s better-than-expected sales outlook helped ease Wall Street concerns about plans for unprecedented spending on artificial intelligence this year. The social networking giant topped projections for holiday quarter revenue and gave a strong forecast for the current period during its earnings report on Jan. 28. Improvements in its online advertising business are making it possible for Meta to spend hundreds of billions of dollars over the next few years on AI infrastructure. Meta’s shares jumped more than 11% in extended trading.Business[#item_full_content]
Over the past decades, computer scientists have developed increasingly advanced artificial intelligence (AI) systems that perform well on various tasks, including the analysis or generation of images, videos, audio recordings and texts. These systems power various highly performing software, including automated transcription apps, large language model (LLM)-powered conversational agents like ChatGPT, and various other platforms.Over the past decades, computer scientists have developed increasingly advanced artificial intelligence (AI) systems that perform well on various tasks, including the analysis or generation of images, videos, audio recordings and texts. These systems power various highly performing software, including automated transcription apps, large language model (LLM)-powered conversational agents like ChatGPT, and various other platforms.Electronics & Semiconductors[#item_full_content]